Patients
Learn about MEG technology, how it can benefit an epilepsy care plan and where to find a MEGIN site.
What is Magnetoencephalograpy (MEG)?
MEG is an exciting technology that detects and records both normal and abnormal brain activity.
It detects the very small magnetic fields that are created when brain cells are active. This can help doctors treat people with epilepsy.
It is quiet, non-invasive, and does not need any injections or radiation. MEG can help doctors decide if a patient would benefit from epilepsy surgery, which may lead to seizure freedom.
Watch this animation to learn more
MEG offers a comfortable patient experience
The MEG scan is safe, calm, and quiet. It is a non-invasive, outpatient visit, lasting only a short time and is safe for both children and adults.
There are no applied magnetic fields, radiation, or injections of any kind. MEG can detect epilepsy activity even when a patient is not having a seizure.
MEG is a very accurate technology and
aids in diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy
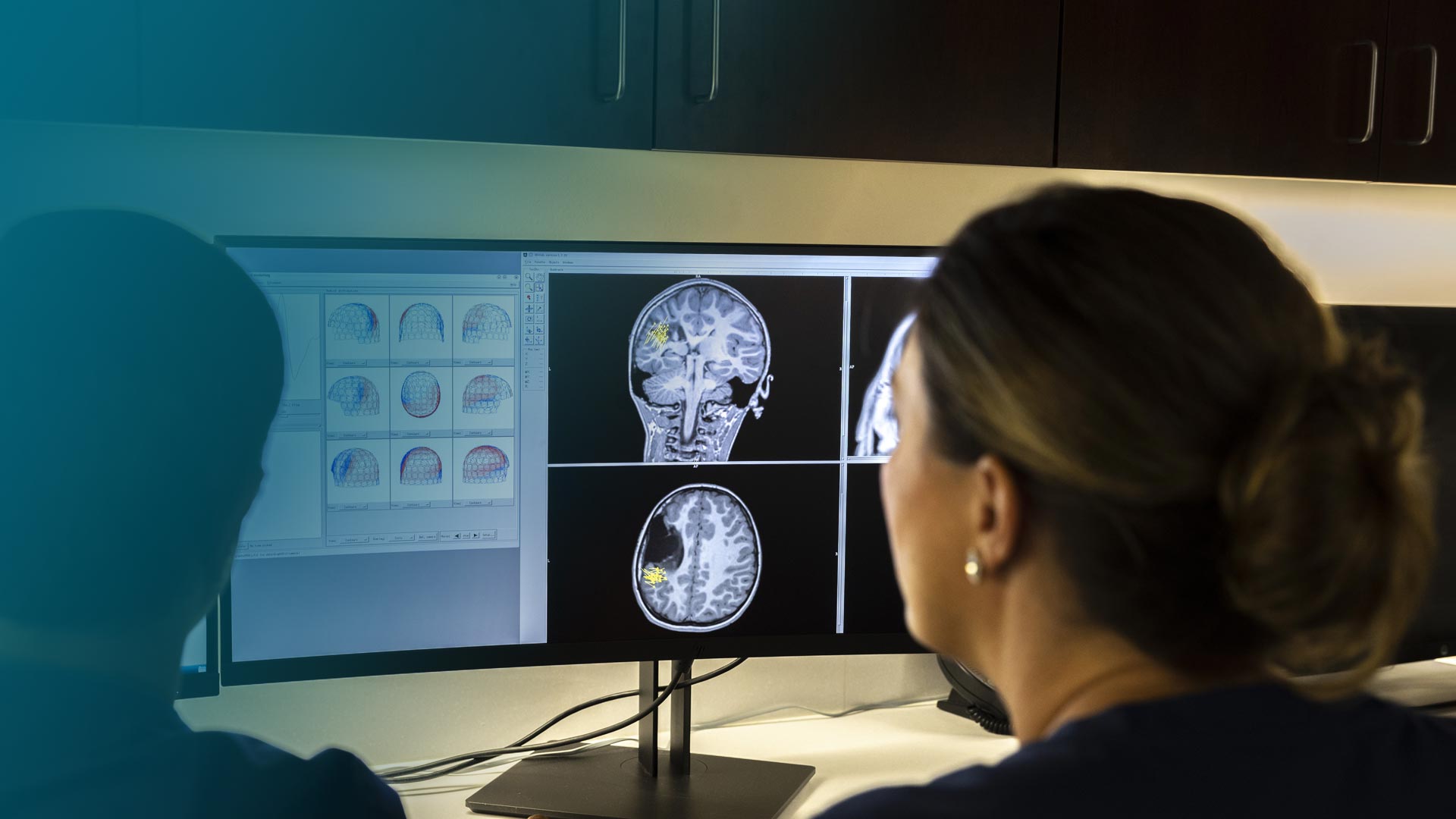
MEG directly measures brain activity on a millisecond-by-millisecond basis. It is not affected by the tissues of the head, so brain function can be localized to within a centimeter or even millimeters of the activity.
MEG helps doctors locate normal brain activity, including where the brain processes language, or sensory information, to help plan treatments. MEG also helps doctors identify abnormal brain activity, including epilepsy activity between seizures.
MEG can help doctors determine if the seizure is coming from only one area of the brain, or if it is more widespread. It helps doctors decide if a patient would benefit from epilepsy surgery, which may lead to seizure freedom.
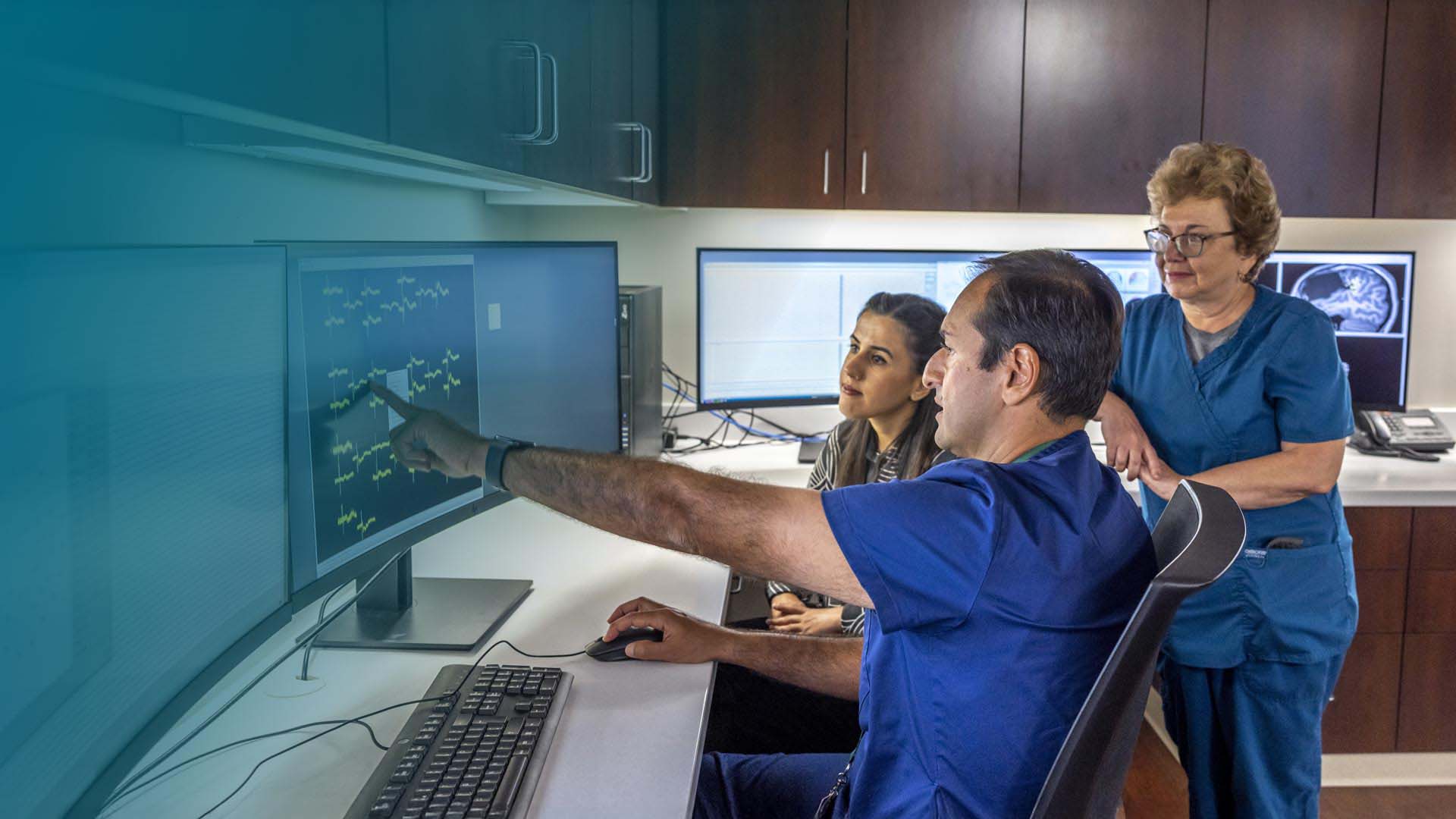

MEG is an important part of pre-surgical evaluation
MEG is used together with structural MRI to show the location of normal and abnormal brain activity. When the MEG scan is read by a doctor, it can be used in treatment planning, specifically, the placement of intercranial EEG (iEEG).
MEG can add new information to the location and understanding of normal and abnormal brain function. It is used alongside other functional brain mapping methods, such as fMRI, PET, SPECT and TMS to assist in presurgical evaluation and treatment planning.
It gives doctors a more complete picture of the location of a patient’s normal and abnormal brain activity, when all the images are used together. This non-invasive technology can enchance the offerings of a comprehensive neuroscience program.
Doctor and caregiver testimonials
Learn more from conversations with caregivers
on our MEGIN Spotlight series